- What is D-FF?
- What is the basic difference between Latches and Flip flops?
- What is a multiplexer?
- How can you convert an SR Flip-flop to a JK Flip-flop?
- How can you convert an JK Flip-flop to a D Flip-flop?
- What is Race-around problem? How can you rectify it?
- Which semiconductor device is used as a voltage regulator and why?
- Explain an ideal voltage source?
- Explain zener breakdown and avalanche breakdown?
- What are the different types of filters?
- What is the need of filtering ideal response of filters and actual response of filters?
- What is sampling theorem?
- What is impulse response?
- Explain the advantages and disadvantages of FIR filters compared to IIR counterparts.
- What is CMRR?
- Explain half-duplex and full-duplex communication?
- Which range of signals is used for terrestrial transmission?
- Why is there need for modulation?
- Which type of modulation is used in TV transmission?
- Why we use vestigial side band (VSB-C3F) transmission for picture?
- When transmitting digital signals is it necessary to transmit some harmonics in addition to fundamental frequency?
- For asynchronous transmission, is it necessary to supply some synchronizing pulses additionally or to supply or to supply start and stop bit?
- BPFSK is more efficient than BFSK in presence of noise. Why?
- What is meant by pre-emphasis and de-emphasis?
- Explain 3 dB cutoff frequency? Why is it 3 dB, not 1 dB?
- Explain ASCII, EBCDIC?
- How to manufacture the CMOS inverter?
- What are the advantages of using C band for satellite communication?
- What frequency bands are used in Satellite Communication?
- what is the difference between latch and flipflop?what is the main difference between 8085 and 8086 processors?
- What is the purpose of the package around a microprocessor silicon die?
- How can we identify how many states the ripple counter is having by looking at the figure as it can also have some invalid states?
- Design gray to binary code converter?
- What is a BCD? What are its advantages and disadvantages? Why is an excess-3 code is called an unweighted code?
Monday, October 6, 2008
General Question on Electronics
Paper 2 Electronics UGCNET
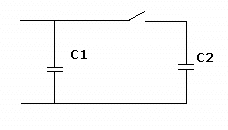
- Two capacitors are connected in parallel through a switch. C1= 1uF, C2= 0.25uF.
Initially the switch is open, C1 is charged to 10V. What happens if we close the switch? No losses in wires and capacitors.
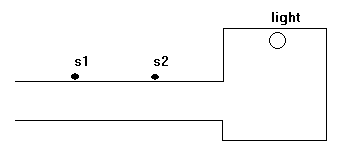
- You have 2 switches to control the light in the long corridor. You want to be able to turn the light on entering the corridor and turn it off at the other end. Do the wiring circuit.
- There are 3 switches that can turn on and off a light in the room. How to connect them?
- What will be the voltage level between the 2 capacitors? The Vcc = 10v DC.

- Suppose, you work on a specification for a system with some digital parameters. The spec table has has Min,Typ and Max colomns for each parameter. In what column would you put a Setup time and a Hold time?
- Design a simple circuit based on combinational logic to double the output frequency.
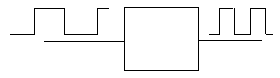
- 8bit ADC with parallel output converts an input signal into digital numbers. You have to come up with an idea of a circuit , that finds MAX of every 10 numbers at the output of the ADC.
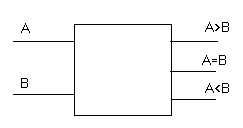
- Implement a comparator that compares two 2-bit numbers A and B. The comparator should have 3 outputs: A > B, A < a =" B.">
- You have a 8 bit ADC clocking data out every 1mS. Design a system that will sort the output data and keep the statistics of how often each binary number appears at the output of ADC.
- What types of flip-flops do you know?
- Implement D- latch from
- RS flip flop;
- multiplexer.
- How to convert D-latch into JK-latch and JK-latch into D-latch?
- There are two counters to 16, built from negedge D- FF . The first circuit is synchronous and the second one is "ripple" (cascading). Which circuit has less propagation delay?
- What is the difference between a flip-flop and a latch?
Write an HDL code for their behavioral models.
- Describe the operation of a DAC. What are the most important parameters of a DAC? Do we really need both INL and DNL to estimate linearity?
- Compare briefly all types of ADC that you know .
- How will the output signal of an ideal integrator look like after
- a positive pulse is applied to the input;
- a series of 10 positive pulses ?
- How to design a divide-by-3 counter with equal duty cycle ?
question from Anonymous
- For an 8-bit flash A/D converter with an input range from 0V to 2.55V, describe what happens when the input voltage changes from 1.27V to 1.28V
- Your system has CPU, ALU and two 8bit registers. There is no external memory. Can you swap the contence of the registers ?
- We swapped 2 transistors in CMOS inverter (put n-transistor at the top and p-transistor at the bottom). Can this circuit work as a non-inverting buffer?
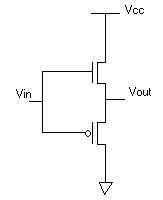
- Convert D-latch into divider by 2.
What is the max clock frequency the circuit can handle ?
T_setup= 6nS
T_hold = 2nS
T_propagation = 10nS
- The circle can rotate clockwise and back. Use minimum hardware to build a circuit to indicate the direction of rotating.
- :An IC device draws higher current when temperature gets:
- higher?
- lower? - To enter the office people have to pass through the corridor. Once someone gets into the office the light turns on. It goes off when noone is present in the room. There are two registration sensors in the corridor. Build a state machine diagram and design a circuit to control the light.
- A voltage source with internal impedance Z_source = 50 OHm is connected to a transmission line with Z = 50 OHm. Z_load is also 50 OHm.
The voltage source generates a single voltage step 1V.
What will be the voltage level on the load:
a) 2V , because the reflected signal will be in-phase with the incident signal;
b) 0.33V , because the voltage is devided between Z_source , Z_load and Z_transm.line;
c) 0.5V , because the voltage is devided between Z_source and Z_load.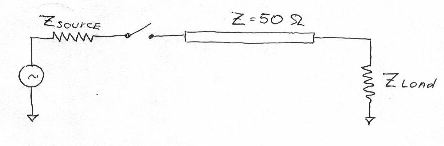
- Draw a transistor schematic of NOR gate,it's layout and a cross section of the layout.
- The silicon of a new device has memory leak. When all "0" are written into RAM, it reads back all "0" whithout any problem. When all "1" are written, only 80% of memory cells are read back correctly. What can be possibly the problem with the RAM?
- Draw a CMOS inverter. Why does CMOS technology dominate in VLSI manufacturing?
- What does CMOS stand for? VLSI? ASIC?
This was in the series of quick questions in the interview at Analog Devices. We use these abbreviations daily, but not everyone remembers what they stand for. - Design a COMBINATIONAL circuit that can divide the clock frequency by 2.
- Design a 2bit up/down counter with clear using gates. (No verilog or vhdl)
- We have a circular wheel with half painted black and the other half painted white. There are 2 censors mounted 45 degree apart at the surface of this wheel( not touching the wheel) which give a "1" for black and "0" for white passing under them. Design a circuit to detect which way the wheel is moving. Can not assume any fixed position for start.
- We have a FIFO which clocks data in at 100mhz and clocks data out at 80mhz. On the input there are only 80 data bits in any order during each 100 clocks. In other words, a 100 input clock will carry only 80 data bits, and the other twenty clocks carry no data (data is scattered in any order). How big the FIFO needs to be to avoid data over/under-run.
- Instead of specifying SETUP and HOLD time, can we just specify a SETUP time for '1' and a SETUP time for '0'?
- Here some hardware digital design specific questions, offered by Suhas:
(1) When will you use a latch and a flipflop in a sequential design?
(2) Design a 1-bit fulladder using a decoder and 2 "or" gates?
(3) You have a circuit operating at 20 MHz and 5 volt supply. What would you do to reduce the power consumption in the circuit- reduce the operating frequency of 20Mhz or reduce the power supply of 5Volts and why?
(4) In a nmos transistor, how does the current flows from drain to source in saturation region when the channel is pinched off?
(5) In a SRAM circuit, how do you design the precharge and how do you size it?
(6) In a PLL, what elements(like XOR gates or Flipflops) can be used to design the phase detector?
(7) While synthesis of a design using synopsys design compiler, why do you specify input and output delays?
(8) What difference do you see in the timing reports for a propogated clock and an ideal clock?
(9) What is timeborrowing related to Static timing anaylsis in Primetime?
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)